partition table對資料維護的效率是一直吸引我的主因,
透過switch partition可說秒殺insert+delete操作,
不僅lock request少,且又可降低交易紀錄檔使用量,整體對我來說好處不少,
但以前經驗告訴我,partition table影響insert和update效能,
我想如果這部分能使用In-Memory table來接管的話那真是太美妙了,可惜In-Memory table並不支援partition,
但我們依然可以透過SQL2016來模擬partition,讓我們同時享有高效率的資料維護和高效能的交易處理。
基本的方向就是hot data使用in-memory table,cold data使用disk table,
而且disk table須為partition table,方便我們透過switch partition將資料轉移到cold’s disk table,
在建立一個view包含hot and cold table,下面我簡單示範。
-- frequently used portion of the SalesOrders - memory-optimized
CREATE TABLE dbo.SalesOrders_hot (
id INT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY NONCLUSTERED,
cust_id INT NOT NULL,
cust_name nvarchar(20) NOT NULL,
so_date DATETIME2 NOT NULL INDEX idx_date NONCLUSTERED,
total MONEY NOT NULL,
INDEX idx_date_total NONCLUSTERED (so_date desc, total desc)
) WITH (MEMORY_OPTIMIZED=ON)
GO
-- cold portion of the SalesOrders - partitioned disk-based table
CREATE PARTITION FUNCTION [ByDatePF](datetime2) AS RANGE RIGHT
FOR VALUES();
GO
CREATE PARTITION SCHEME [ByDateRange]
AS PARTITION [ByDatePF]
ALL TO ([PRIMARY]);
GO
CREATE TABLE dbo.SalesOrders_cold (
id INT NOT NULL,
cust_id INT NOT NULL,
cust_name nvarchar(20) NOT NULL,
so_date DATETIME2 NOT NULL,
total MONEY NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_SalesOrders_cold PRIMARY KEY (id, so_date),
INDEX idx_date_total NONCLUSTERED (so_date desc, total desc)
) ON [ByDateRange](so_date)
GO
-- table for temporary partitions
CREATE TABLE dbo.SalesOrders_cold_staging (
id INT NOT NULL,
cust_id INT NOT NULL,
cust_name nvarchar(20) NOT NULL,
so_date datetime2 NOT NULL,
total MONEY NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_SalesOrders_cold_staging PRIMARY KEY (id, so_date),
INDEX idx_date_total NONCLUSTERED (so_date desc, total desc),
CONSTRAINT CHK_SalesOrders_cold_staging CHECK (so_date >= '2000-01-01')
)
GO
-- aggregate view of the hot and cold data
CREATE VIEW dbo.uvSalesOrders
AS SELECT id,
cust_id,
cust_name,
so_date,
total,
1 AS 'is_hot'
FROM dbo.SalesOrders_hot
UNION ALL
SELECT id,
cust_id,
cust_name,
so_date,
total,
0 AS 'is_hot'
FROM dbo.SalesOrders_cold;
GO
-- move all sales orders up to the split date to cold storage
CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.usp_SalesOrdersOffloadToCold @splitdate datetime2
AS
BEGIN
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
-- create new heap based on the hot data to be moved to cold storage
INSERT INTO dbo.SalesOrders_cold_staging WITH( TABLOCKX)
SELECT id , cust_id ,cust_name, so_date , total
FROM dbo.SalesOrders_hot WITH ( serializable)
WHERE so_date <= @splitdate;
-- remove moved data
DELETE FROM dbo.SalesOrders_hot WITH( serializable)
WHERE so_date <= @splitdate;
-- update partition function, and switch in new partition
ALTER PARTITION SCHEME [ByDateRange] NEXT USED [PRIMARY];
DECLARE @p INT = ( SELECT MAX( partition_number) FROM sys.partitions WHERE object_id = OBJECT_ID( 'dbo.SalesOrders_cold'));
EXEC sp_executesql N'alter table dbo.SalesOrders_cold_staging
SWITCH TO dbo.SalesOrders_cold partition @i' , N'@i int' , @i = @p;
ALTER PARTITION FUNCTION [ByDatePF]()
SPLIT RANGE( @splitdate);
-- modify constraint on staging table to align with new partition
ALTER TABLE dbo.SalesOrders_cold_staging DROP CONSTRAINT CHK_SalesOrders_cold_staging;
DECLARE @s nvarchar( 100) = CONVERT( nvarchar( 100) , @splitdate , 121);
DECLARE @sql nvarchar( 1000) = N'alter table dbo.SalesOrders_cold_staging
add constraint CHK_SalesOrders_cold_staging check (so_date > ''' + @s + ''')';
PRINT @sql;
EXEC sp_executesql @sql;
COMMIT;
END;
GO
/** DEMO **/
-- insert sample values in the hot table
INSERT INTO dbo.SalesOrders_hot VALUES(1,'ricoisme',SYSDATETIME(), 1)
,(1,'ricoisme', SYSDATETIME(), 1) ,(1,'ricoisme', SYSDATETIME(), 1)
,(2,'ricoisme', SYSDATETIME(), 1)
,(2,'ricoisme', SYSDATETIME(), 1),(2,'ricoisme', SYSDATETIME(), 1)
GO
-- verify contents of the table
SELECT * FROM dbo.uvSalesOrders;
GO
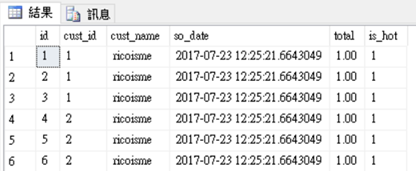
-- offload all sales orders to date to cold storage
DECLARE @t datetime2 = SYSDATETIME();
EXEC dbo.usp_SalesOrdersOffloadToCold @t;
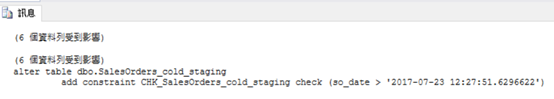
-- verify contents of the tables
SELECT * FROM dbo.uvSalesOrders;
GO
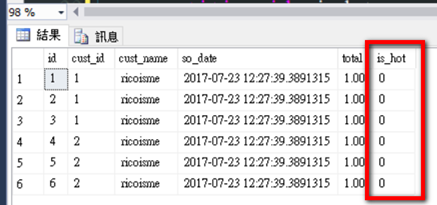
-- verify partitions
SELECT t.name AS TableName, i.name AS IndexName,r.value AS BoundaryValue , p.partition_number,p.rows
,p.partition_id, i.data_space_id, f.function_id, f.type_desc, r.boundary_id
FROM sys.tables AS t
JOIN sys.indexes AS i
ON t.object_id = i.object_id
JOIN sys.partitions AS p
ON i.object_id = p.object_id AND i.index_id = p.index_id
JOIN sys.partition_schemes AS s
ON i.data_space_id = s.data_space_id
JOIN sys.partition_functions AS f
ON s.function_id = f.function_id
LEFT JOIN sys.partition_range_values AS r
ON f.function_id = r.function_id and r.boundary_id = p.partition_number
WHERE t.name = 'SalesOrders_cold' AND i.type <= 1
ORDER BY p.partition_number;
參考
[SQL SERVER][Memo]打造動態Partition Table
[SQL SERVER]Partition Table一定提高查詢效能?
[SQL SERVER][Performance]善用Partition Table#1簡介
[SQL SERVER][TSQL] 查詢 Partition Table 相關資訊
Transactions with Memory-Optimized Tables
Application-Level Partitioning
Application Pattern for Partitioning Memory-Optimized Tables
[SQL SERVER][Tools]善用 Partition Management Utility