[VISIO]透過VISIO Automation建立組織圖
前言
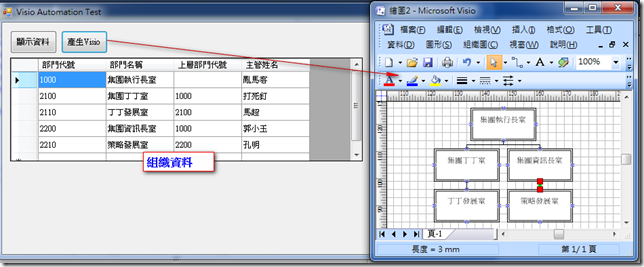
因為客戶常常需要將資料轉到Visio之中,我們都是將資料轉出到Excel後,再請User從Visio轉入產生組織圖,所以就想說直接產生Visio圖給User。
從網站上查看Visio的開發資料還蠻少的,只有CodeProject中的一篇文章在談,其他就都是Link到Visio的SDK。
需求
需求是給一個單位的DataTable,然後產生Visio的組織圖。
實作
1.先建立單位的資料,一般會有單位代號、名稱、上層單位代號及主管姓名,如下,
/// <summary>
/// 產生部門清單資料
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private DataTable GetDeptList()
{
DataTable deptList = new DataTable("DEPT_LIST");
deptList.Columns.Add("部門代號", Type.GetType("System.String"));
deptList.Columns.Add("部門名稱", Type.GetType("System.String"));
deptList.Columns.Add("上層部門代號", Type.GetType("System.String"));
deptList.Columns.Add("主管姓名", Type.GetType("System.String"));
deptList.Rows.Add(new string[] { "1000", "集團執行長室", "", "亂馬客" });
deptList.Rows.Add(new string[] { "2100", "集團丁丁室", "1000", "打死釘" });
deptList.Rows.Add(new string[] { "2110", "丁丁發展室", "2100", "馬超" });
deptList.Rows.Add(new string[] { "2200", "集團資訊長室", "1000", "郭小玉" });
deptList.Rows.Add(new string[] { "2210", "策略發展室", "2200", "孔明" });
return deptList;
}
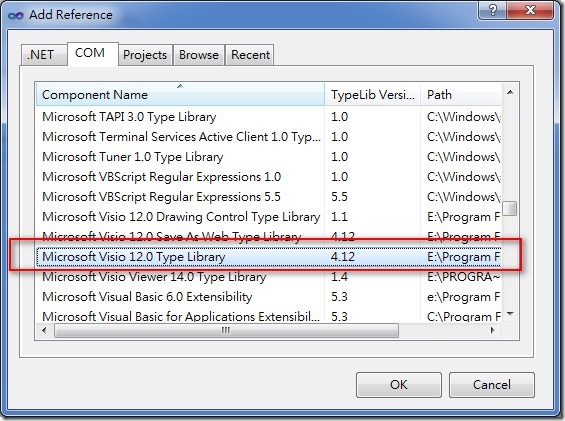
2.參考Visio的SDK,建立Visio Automation物件,來建立組織圖(範例中VisioRef.cs)。
Application visioApp = new Application();
Document visioDoc = visioApp.Documents.Add(VisioORGVST);
Page visioPage = visioApp.Documents[1].Pages[1];
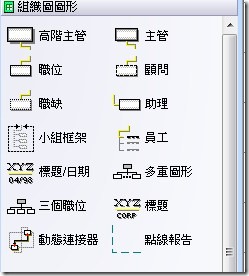
3.有了Page後,就可以選取組織圖中的圖形(高階主管、主管、職位、顧問....),這裡使用的是主管這個圖。
//建立Manager圖形
Master visioMaster = visioDoc.Masters.ItemU["Manager"];
//將圖形拉到Page上
Shape visioShape = visioPage.Drop(visioMaster, xPos, yPos - level);
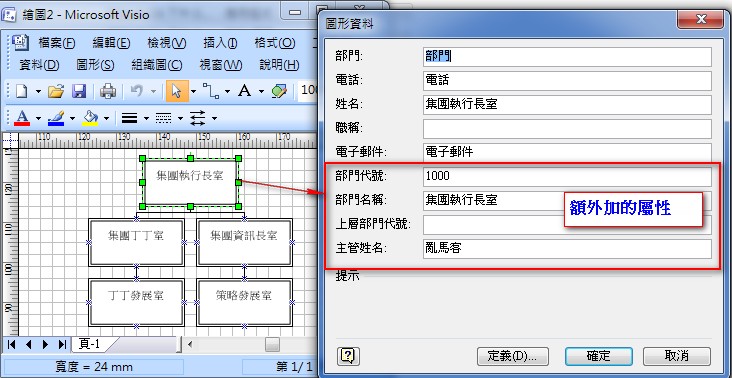
4.因為有其他的屬性要加入,所以呼叫AddCustomProperties去加入各欄位,而只要加入一個圖形的屬性,其他圖形也會有那些屬性哦!
//依資料表的欄位,加入屬性
AddCustomProperties(visioShape);
5.然後依資料設定圖形屬性(BindDeptData2Shape),SetCustomPropertyValue是SDK提供的設定圖形的屬性。
/// <summary>
/// 將資料Assign到圖形之中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="shape"></param>
/// <param name="deptInfo"></param>
private void BindDeptData2Shape(Shape shape, DataRow deptInfo)
{
foreach (System.Data.DataColumn dc in OrgRecordList.Columns)
{
SetCustomPropertyValue(shape, dc.ColumnName, (string)deptInfo[dc.ColumnName], VisUnitCodes.visUnitsString);
if (dc.ColumnName == "部門名稱")
{
shape.Text = (string)deptInfo[dc.ColumnName];
}
}
}
6.再來建立出下層單位同時建立父子單的關連。
//建立關連
ConnectWithDynamicGlueAndConnector(parentShape, deptShape);
7.最後再呼叫Visio Page的Layout Method重新排列圖形。
//請Visio重新排列圖形
visioPage.Layout();
完整的VisioRef.cs如下,
/// <summary>
/// 使用Visio建立組織圖
/// </summary>
class VisioRef
{
//篩選部門條件
const string FilterParent = "[上層部門代號] = '{0}'";
//組織圖
const string VisioORGVST = "ORGCH_M.VST";
//Visio Application Prog Id
const string VisioApplicationId = "Visio.Application";
//單位的資料
public DataTable OrgRecordList;
//要產生組織圖資料的最上層單位代號
public string RootParentCode = string.Empty;
/// <summary>
/// 產生組織圖
/// </summary>
public void GenerateDiagram()
{
Application visioApp = new Application();
Document visioDoc = visioApp.Documents.Add(VisioORGVST);
Page visioPage = visioApp.Documents[1].Pages[1];
DataRow[] rootDeptList = OrgRecordList.Select(string.Format(FilterParent, RootParentCode));
int rootCount = rootDeptList.Length;
double xPos = visioPage.PageSheet.CellsU["PageWidth"].ResultIU / rootCount + 1;
int level = 1;
double yPos = visioPage.PageSheet.CellsU["PageHeight"].ResultIU - 1;
foreach (DataRow drData in rootDeptList)
{
//建立Manager圖形
Master visioMaster = visioDoc.Masters.ItemU["Manager"];
//將圖形拉到Page上
Shape visioShape = visioPage.Drop(visioMaster, xPos, yPos - level);
//依資料表的欄位,加入屬性
AddCustomProperties(visioShape);
//將資料Assign到圖形之中
BindDeptData2Shape(visioShape, drData);
xPos += 1.5;
//拉出下層部門
DrawChildDept((string)drData["部門代號"], visioShape, xPos, level);
}
//請Visio重新排列圖形
visioPage.Layout();
}
/// <summary>
/// 拉出下層部門
/// </summary>
private void DrawChildDept(string parentDeptCode, Shape parentShape, double xPos, int level)
{
double yPos = parentShape.ContainingPage.PageSheet.CellsU["PageHeight"].ResultIU - 1;
//找出單位清單
DataRow[] deptList = OrgRecordList.Select(string.Format(FilterParent, parentDeptCode));
foreach (DataRow drData in deptList)
{
xPos += 1.5;
Master deptMaster = parentShape.Document.Masters.ItemU["Manager"];
Shape deptShape = parentShape.ContainingPage.Drop(deptMaster, xPos, yPos - level);
//將資料Assign到圖形之中
BindDeptData2Shape(deptShape, drData);
//建立關連
ConnectWithDynamicGlueAndConnector(parentShape, deptShape);
//拉出下層部門
DrawChildDept((string)drData["部門代號"], deptShape, xPos, level + 1);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 將資料Assign到圖形之中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="shape"></param>
/// <param name="deptInfo"></param>
private void BindDeptData2Shape(Shape shape, DataRow deptInfo)
{
foreach (System.Data.DataColumn dc in OrgRecordList.Columns)
{
SetCustomPropertyValue(shape, dc.ColumnName, (string)deptInfo[dc.ColumnName], VisUnitCodes.visUnitsString);
if (dc.ColumnName == "部門名稱")
{
shape.Text = (string)deptInfo[dc.ColumnName];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 依資料加入屬性
/// </summary>
/// <param name="rootShape"></param>
private void AddCustomProperties(Shape rootShape)
{
foreach (System.Data.DataColumn dc in OrgRecordList.Columns)
{
AddCustomProperty(rootShape, dc.ColumnName, dc.ColumnName, dc.ColumnName, Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.VisCellVals.visPropTypeString, string.Empty, string.Empty, false, false, string.Empty );
}
}
#region "Visio SDK "
/// <summary>This method creates a custom property for the shape that
/// is passed in as a parameter.</summary>
/// <param name="addedToShape">Shape to which the custom property is
/// to be added</param>
/// <param name="localRowName">Local name for the row. This name will
/// appear in custom properties dialog for users running in developer
/// mode.</param>
/// <param name="rowNameU">Universal name of the custom property to be
/// created</param>
/// <param name="labelName">Label of the custom property</param>
/// <param name="propType">Type of the value of the custom property.
/// Not all VisCellVals constants are valid for this parameter. Only
/// constants that start with visPropType make sense in this context.
/// </param>
/// <param name="format">Format of the custom property</param>
/// <param name="prompt">Prompt for the custom property</param>
/// <param name="askOnDrop">Value of the "Ask On Drop" check box of the
/// custom property. Only seen in developer mode</param>
/// <param name="hidden">Value of the "Hidden" check box of the custom
/// property. Only seen in developer mode</param>
/// <param name="sortKey">Value of the Sort key of the custom property.
/// Only seen in developer mode</param>
/// <returns>True if successful; false otherwise</returns>
public bool AddCustomProperty(
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Shape addedToShape,
string localRowName,
string rowNameU,
string labelName,
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.VisCellVals propType,
string format,
string prompt,
bool askOnDrop,
bool hidden,
string sortKey)
{
const string CUST_PROP_PREFIX = "Prop.";
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Cell shapeCell;
short rowIndex;
bool returnValue = false;
if (addedToShape == null)
{
return false;
}
try
{
// Add a named custom property row. In addition to adding a row
// with the local name, specified via localRowName parameter,
// this call will usually set the universal name of the new row
// to localRowName as well. However, the universal row name
// will not be set if this shape already has a custom property
// row that has the universal name equal to localRowName.
rowIndex = addedToShape.AddNamedRow(
(short)(Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisSectionIndices.visSectionProp),
localRowName, (short)(Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisRowIndices.visRowProp));
// The columns of the properties to set are fixed and can be
// accessed directly using the CellsSRC method and column index.
// Get the Cell object for each one of the items in the
// custom property and set its value using the FormulaU property
// of the Cell object.
// Column 1 : Prompt
shapeCell = addedToShape.get_CellsSRC(
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisSectionIndices.visSectionProp, rowIndex,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisCellIndices.visCustPropsPrompt);
SetCellValueToString(shapeCell,
prompt);
// Any cell in the row can be used to set the universal
// row name. Only set the name if rowNameU parameter differs
// from the local name and is not blank.
if (rowNameU != null)
{
if ((localRowName != rowNameU) && (rowNameU.Length > 0))
{
shapeCell.RowNameU = rowNameU;
}
}
// Column 2 : Label
shapeCell = addedToShape.get_CellsSRC(
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisSectionIndices.visSectionProp, rowIndex,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisCellIndices.visCustPropsLabel);
SetCellValueToString(shapeCell,
labelName);
// Column 3 : Format
shapeCell = addedToShape.get_CellsSRC(
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisSectionIndices.visSectionProp, rowIndex,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisCellIndices.visCustPropsFormat);
SetCellValueToString(shapeCell,
format);
// Column 4 : Sort Key
//shapeCell = addedToShape.get_CellsSRC(
// (short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
// VisSectionIndices.visSectionProp, rowIndex,
// (short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
// VisCellIndices.visCustPropsSortKey);
//formatHelper.SetCellValueToString(shapeCell,
// sortKey);
// Column 5 : Type
//shapeCell = addedToShape.get_CellsSRC(
// (short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
// VisSectionIndices.visSectionProp, rowIndex,
// (short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
// VisCellIndices.visCustPropsType);
//formatHelper.SetCellValueToString(shapeCell,
// ((short)propType).ToString(
// System.Globalization.CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
// Column 6 : Hidden (This corresponds to the invisible cell in
// the Shapesheet)
shapeCell = addedToShape.get_CellsSRC(
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisSectionIndices.visSectionProp, rowIndex,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisCellIndices.visCustPropsInvis);
SetCellValueToString(shapeCell,
hidden.ToString(
System.Globalization.CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
//// Column 7 : Ask on drop
//shapeCell = addedToShape.get_CellsSRC(
// (short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
// VisSectionIndices.visSectionProp, rowIndex,
// (short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
// VisCellIndices.visCustPropsAsk);
//formatHelper.SetCellValueToString(shapeCell,
// askOnDrop.ToString(
// System.Globalization.CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
// Set the custom property for the shape using FormulaU
// property of the cell.
shapeCell = addedToShape.get_CellsU(CUST_PROP_PREFIX
+ rowNameU);
SetCellValueToString(shapeCell,
rowNameU);
returnValue = true;
}
catch (Exception err)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(err.Message);
throw;
}
return returnValue;
}
/// <summary>This method converts the input string to a Visio string by
/// replacing each double quotation mark (") with a pair of double
/// quotation marks ("") and then adding double quotation marks around
/// the entire string.</summary>
/// <param name="inputValue">Input string that will be converted
/// to Visio String</param>
/// <returns>Converted Visio string</returns>
public static string StringToFormulaForString(string inputValue)
{
string result = "";
string quote = "\"";
string quoteQuote = "\"\"";
try
{
result = inputValue != null ? inputValue : String.Empty;
// Replace all (") with ("").
result = result.Replace(quote, quoteQuote);
// Add ("") around the whole string.
result = quote + result + quote;
}
catch (Exception err)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(err.Message);
throw;
}
return result;
}
/// <summary>This method sets the value of the specified Visio cell
/// to the new string passed as a parameter.</summary>
/// <param name="formulaCell">Cell in which the value is to be set
/// </param>
/// <param name="newValue">New string value that will be set</param>
public void SetCellValueToString(
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Cell formulaCell,
string newValue)
{
try
{
// Set the value for the cell.
formulaCell.FormulaU = StringToFormulaForString(newValue);
}
catch (Exception err)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(err.Message);
throw;
}
}
/// <summary>This method accesses the Basic Flowchart Shapes stencil and
/// the dynamic connector master on the stencil. It connects two 2-D
/// shapes using the dynamic connector by gluing the connector to the
/// PinX cells of the 2-D shapes to create dynamic (walking) glue.
///
/// Note: To get dynamic glue, a dynamic connector must be used and
/// connected to the PinX or PinY cell of the 2-D shape.
/// For more information about dynamic glue, see the "Working with 1-D
/// Shapes, Connectors, and Glue" section in the book, Developing
/// Microsoft Visio Solutions.</summary>
/// <param name="shapeFrom">Shape from which the dynamic connector
/// begins</param>
/// <param name="shapeTo">Shape at which the dynamic connector ends
/// </param>
public void ConnectWithDynamicGlueAndConnector(
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Shape shapeFrom,
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Shape shapeTo)
{
if (shapeFrom == null || shapeTo == null)
{
return;
}
const string BASIC_FLOWCHART_STENCIL =
"Basic Flowchart Shapes (US units).vss";
const string DYNAMIC_CONNECTOR_MASTER = "Dynamic Connector";
const string MESSAGE_NOT_SAME_PAGE =
"Both the shapes are not on the same page.";
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Application visioApplication;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Document stencil;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Master masterInStencil;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Shape connector;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Cell beginX;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Cell endX;
// Get the Application object from the shape.
visioApplication = (Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Application)
shapeFrom.Application;
try
{
// Verify that the shapes are on the same page.
if (shapeFrom.ContainingPage != null && shapeTo.ContainingPage != null &&
shapeFrom.ContainingPage.Equals(shapeTo.ContainingPage))
{
// Access the Basic Flowchart Shapes stencil from the
// Documents collection of the application.
stencil = visioApplication.Documents.OpenEx(
BASIC_FLOWCHART_STENCIL,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisOpenSaveArgs.visOpenDocked);
// Get the dynamic connector master on the stencil by its
// universal name.
masterInStencil = stencil.Masters.get_ItemU(
DYNAMIC_CONNECTOR_MASTER);
// Drop the dynamic connector on the active page.
connector = visioApplication.ActivePage.Drop(
masterInStencil, 0, 0);
// Connect the begin point of the dynamic connector to the
// PinX cell of the first 2-D shape.
beginX = connector.get_CellsSRC(
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisSectionIndices.visSectionObject,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisRowIndices.visRowXForm1D,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisCellIndices.vis1DBeginX);
beginX.GlueTo(shapeFrom.get_CellsSRC(
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisSectionIndices.visSectionObject,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisRowIndices.visRowXFormOut,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisCellIndices.visXFormPinX));
// Connect the end point of the dynamic connector to the
// PinX cell of the second 2-D shape.
endX = connector.get_CellsSRC(
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisSectionIndices.visSectionObject,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisRowIndices.visRowXForm1D,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisCellIndices.vis1DEndX);
endX.GlueTo(shapeTo.get_CellsSRC(
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisSectionIndices.visSectionObject,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisRowIndices.visRowXFormOut,
(short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisCellIndices.visXFormPinX));
}
else
{
// Processing cannot continue because the shapes are not on
// the same page.
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(MESSAGE_NOT_SAME_PAGE);
}
}
catch (Exception err)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(err.Message);
throw;
}
}
/// <summary> This method accesses the custom property Value cell and
/// sets the formula in that cell to the string in the
/// universalSyntaxFormula parameter. When the formula is set, Visio
/// evaluates the formula to determine the result for that cell. If the
/// formula creates dependencies on other cells, the value of the custom
/// property will change when those cells change.</summary>
/// <param name="customPropertyShape">Shape that has the custom
/// property</param>
/// <param name="rowNameU">Universal name of the custom property to be
/// accessed</param>
/// <param name="universalSyntaxFormula">Value to be assigned to the
/// custom property</param>
public void SetCustomPropertyFormula(
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Shape customPropertyShape,
string rowNameU,
string universalSyntaxFormula)
{
if (customPropertyShape == null || rowNameU == null
|| universalSyntaxFormula == null)
{
return;
}
const string CUST_PROP_PREFIX = "Prop.";
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Cell customPropertyCell;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Application visioApplication =
(Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Application)
customPropertyShape.Application;
try
{
// Verify that all incoming string parameters are not of zero
// length, except for the ones that have default values as ""
// and the output parameters.
if (rowNameU.Length == 0)
{
throw new System.ArgumentNullException("rowNameU",
"Zero length string input.");
}
if (universalSyntaxFormula.Length == 0)
{
throw new System.ArgumentNullException(
"universalSyntaxFormula", "Zero length string input.");
}
// Check to see if the shape has custom property Value cell
// with this universal row name. If no cell exists display
// an error message and exit this method.
if (customPropertyShape.get_CellExistsU(CUST_PROP_PREFIX +
rowNameU, (short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisExistsFlags.visExistsLocally) == 0)
{
if (visioApplication.AlertResponse == 0)
{
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(
"This shape does not have a custom property"
+ "\r\nwith the universal name '" + rowNameU
+ "'.");
}
return;
}
// Get the Cell object. Note the addition of "Prop." to the
// name given to the cell.
customPropertyCell = customPropertyShape.get_CellsU(
CUST_PROP_PREFIX + rowNameU);
// To see how this method works, try several different
// formula parameters. For example, if the formula is "5*12"
// then the value of the custom property Value cell will be
// set to 60. Also, try the formula: "Width * 2". In this
// case, the value of the custom property will be set to
// the value of the current width times 2 AND the custom
// property value will change when the width of the shape
// changes.
customPropertyCell.FormulaU = universalSyntaxFormula;
}
catch (Exception err)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(err.Message);
throw;
}
}
/// <summary>This method assigns a value to a custom property cell with
/// the universal row name, specified via rowNameU parameter, in the
/// shape, specified via shape parameter, using the value and units
/// passed in as parameters.</summary>
/// <param name="customPropertyShape">Shape which has the custom
/// property</param>
/// <param name="rowNameU">Universal name of the custom property</param>
/// <param name="propertyValue">Value of the custom property</param>
/// <param name="units">Units of the value of the custom property
/// </param>
public void SetCustomPropertyValue(
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Shape customPropertyShape,
string rowNameU,
object propertyValue,
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.VisUnitCodes units)
{
if (customPropertyShape == null || propertyValue == null ||
rowNameU == null)
{
return;
}
const string CUST_PROP_PREFIX = "Prop.";
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Application visioApplication =
(Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Application)
customPropertyShape.Application;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.Cell customPropertyCell;
try
{
// Verify that all incoming string parameters are not of zero
// length, except for the ones that have default values as ""
// and the output parameters.
if (rowNameU.Length == 0)
{
throw new System.ArgumentNullException("rowNameU",
"Zero length string input.");
}
// See if the shape has a custom property Value cell with the
// universal row name. If no cell exists, display an error
// message and exit this method.
if ((customPropertyShape.get_CellExistsU(CUST_PROP_PREFIX +
rowNameU, (short)Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.
VisExistsFlags.visExistsLocally)) == 0)
{
if (visioApplication.AlertResponse == 0)
{
System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox.Show(
"This shape does not have a Custom Property\r\n" +
"with the universal name '" + rowNameU + "'.");
}
}
else
{
// Get the Cell object. Note the addition of "Prop."
// to the name given to the cell.
customPropertyCell = customPropertyShape.get_CellsU(
CUST_PROP_PREFIX + rowNameU);
if (units == Microsoft.Office.Interop.Visio.VisUnitCodes.
visUnitsString)
{
SetCellValueToString(customPropertyCell,
propertyValue.ToString());
}
else
{
// Use the set_Result method to set values other than
// string type.
customPropertyCell.set_Result(units,
Convert.ToDouble(propertyValue,
System.Globalization.CultureInfo.InvariantCulture));
}
}
}
catch (Exception err)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(err.Message);
throw;
}
}
#endregion
}
結論
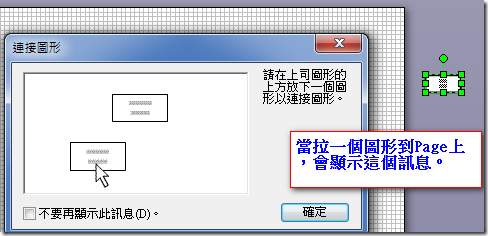
1.雖然建立了組織圖,但在將圖形拉到Page上時,Visio會顯示以下的訊息及如何設定Page預設的顯示屬性。有進一步資訊再補充。
2.如果要在不同版本的Visio使用的話,可以不用加入Visio的參考,而改直接使用CreateObject("Visio.Application")的方式來操作Visio。
參考資料
範例
Hi,
亂馬客Blog已移到了 「亂馬客 : Re:從零開始的軟體開發生活」
請大家繼續支持 ^_^