[C#][Control]BitsControl概念與簡易實做
有些人可能還看不出前一篇指撥開關的用途,其實做些變化指撥開關還可以用來做些簡易的硬體設定。像是做個控制項可以載入一個Byte的資料,並允許使用者直接去調整設定,可用在GPIB、I2C之類的通訊界面設定,設定一些位置資訊。
實作時可建立一個新的使用者控制項,在裡面加入FlowLayoutPanel控制項,再加入八個SwitchButton,與一個Panel去分隔。這邊可將控制項的BorderStyle設為FixedSingle,整個控制項比較會有一體的感覺。
接著必須在整個控制項SizeChanged時調整裡面的SwitchButton大小,這樣做出來的控制項才能適應不同的大小。
private void BitsControl_SizeChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int width = flowLayoutPanel1.ClientSize.Width - panel1.Width - bit8.Margin.Left * 16 - panel1.Margin.Left * 2;
if(width < 0)
return;
int bitWith = width / 8;
bit8.Width = bitWith;
bit7.Width = bitWith;
bit6.Width = bitWith;
bit5.Width = bitWith;
bit4.Width = bitWith;
bit3.Width = bitWith;
bit2.Width = bitWith;
bit1.Width = bitWith;
int bitHeight = flowLayoutPanel1.ClientSize.Height - bit8.Margin.Top * 2;
bit8.Height = bitHeight;
bit7.Height = bitHeight;
bit6.Height = bitHeight;
bit5.Height = bitHeight;
bit4.Height = bitHeight;
bit3.Height = bitHeight;
bit2.Height = bitHeight;
bit1.Height = bitHeight;
}
接著必須為控制項加入最主要的功能,也就是必須要能讓它載入權重值或是HexString,依不同的設定值調整SwitchButton。這部分的實作也很簡單,只要從高權位的開始處理,若是目前剩餘的權重值高過當前SwitchButton的權重值,代表當前的SwitchButton應該調為On的狀態,並將目前剩餘的權重值扣掉當前SwitchButton的權重值,不然則調為Off的狀態。
public void LoadBitsState(int weightValue)
{
SwitchButton[] switchButtons = { bit1, bit2, bit3, bit4, bit5, bit6, bit7, bit8 };
for (int i = 8; i >= 1; --i)
{
int currentWeightValue = int.Parse(Math.Pow(2 , i - 1).ToString());
SwitchButton currentSwitchButton = switchButtons[i - 1];
if (weightValue >= currentWeightValue)
{
currentSwitchButton.State = SwitchButton.SwitchState.On;
weightValue -= currentWeightValue;
}
else
{
currentSwitchButton.State = SwitchButton.SwitchState.Off;
}
}
}
public void LoadBitsState(string hexValue)
{
LoadBitsState(Convert.ToInt32(hexValue, 16));
}
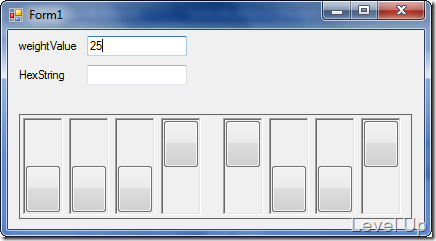
簡易的實作到這邊已經完成了,實際運行時會整個控制項會像下面這樣。
這邊只是個簡易的範例,當然在實際運用時可能必須視需要將權重值或是HexString開出,並能讓使用者透過介面選取適時的影響取回的權重值或是HexString。
最後這邊附上較為完整的程式碼:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication6
{
public partial class BitsControl : UserControl
{
public BitsControl()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
public void LoadBitsState(int weightValue)
{
SwitchButton[] switchButtons = { bit1, bit2, bit3, bit4, bit5, bit6, bit7, bit8 };
for (int i = 8; i >= 1; --i)
{
int currentWeightValue = int.Parse(Math.Pow(2 , i - 1).ToString());
SwitchButton currentSwitchButton = switchButtons[i - 1];
if (weightValue >= currentWeightValue)
{
currentSwitchButton.State = SwitchButton.SwitchState.On;
weightValue -= currentWeightValue;
}
else
{
currentSwitchButton.State = SwitchButton.SwitchState.Off;
}
}
}
public void LoadBitsState(string hexValue)
{
LoadBitsState(Convert.ToInt32(hexValue, 16));
}
private void BitsControl_SizeChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int width = flowLayoutPanel1.ClientSize.Width - panel1.Width - bit8.Margin.Left * 16 - panel1.Margin.Left * 2;
if(width < 0)
return;
int bitWith = width / 8;
bit8.Width = bitWith;
bit7.Width = bitWith;
bit6.Width = bitWith;
bit5.Width = bitWith;
bit4.Width = bitWith;
bit3.Width = bitWith;
bit2.Width = bitWith;
bit1.Width = bitWith;
int bitHeight = flowLayoutPanel1.ClientSize.Height - bit8.Margin.Top * 2;
bit8.Height = bitHeight;
bit7.Height = bitHeight;
bit6.Height = bitHeight;
bit5.Height = bitHeight;
bit4.Height = bitHeight;
bit3.Height = bitHeight;
bit2.Height = bitHeight;
bit1.Height = bitHeight;
}
}
}