[.NET Concept]throw V.S throw ex
在例外處理時,有些情況下我們會需要將例外攔截後再次向外擴,在此時我們有兩種可選擇的寫法,一種是很多初學者會採用的透過throw ex來外擴例外,這種寫法須避免使用,因為採用此種寫法會改變的原來的呼叫堆疊,造成除錯上的困難。
{
// do something
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// do something
throw ex;
}另一種則是直接透過throw來外擴,跟throw ex不同的是,採用這種方法在外擴例外的同時仍可保留原有的呼叫堆疊。
{
// do something
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// do something
throw;
}
這邊來看個較為完整的範例:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace ConsoleApplication6
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
TestThrow();
TestThrowEx();
}
static void ThrowException()
{
throw new Exception();
}
static void TestThrow()
{
try
{
try
{
ThrowException();
}
catch (Exception)
{
throw;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("TestThrow");
Console.WriteLine(ex.StackTrace);
Console.WriteLine(new string('=',50));
}
}
static void TestThrowEx()
{
try
{
try
{
ThrowException();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("TestThrowEx");
Console.WriteLine(ex.StackTrace);
Console.WriteLine(new string('=', 50));
}
}
}
}
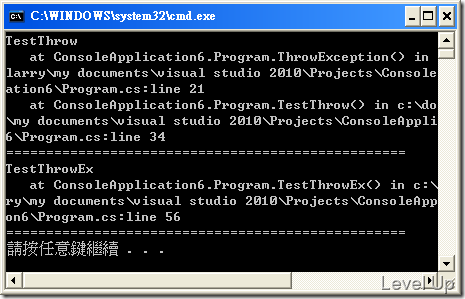
其運行結果如下:
從運行結果我們可以看出直接呼叫throw外擴例外的方法,其呼叫堆疊仍舊保留有外擴前的呼叫堆疊資訊,而呼叫throw ex外擴例外的方法,則只剩下外擴後的呼叫堆疊,外擴前的呼叫堆疊資訊會被覆寫掉,透過呼叫堆疊只能追到外擴的點,看不到例外發生的源頭,造成後續我們使用呼叫堆疊去找尋錯誤的困難。