[ASP.NET]重構之路系列v10 –責任鏈模式的應用
前言
今天這篇主要要說明的,是責任鏈模式的應用(要說變形也可以)。
責任鏈的精神,簡單的說,就是:『阿星,接力!接力!』就像接力賽一樣,把一陀事情抽象來看,轉成對應的物件所擁有的抽象方法,並由使用場景定義好,這些物件的接棒順序。
整個物件的合作過程,就像安排大隊接力一樣,每個物件就像每個選手,只要負責用自己的方式,跑完自己的責任,並察看是不是有下一個接棒者,若有則交棒。
需求說明
- 背景是應徵者來面試,依據應徵者應徵職位的不同,來決定面試官的組成與面試的順序。
- 每一個面試官面試的方式跟評分的重點不一樣。
- 未來可能會有調整面試官組成或面試順序的情況。
- 未來開放的職缺職位也可能會增加,相對應的面試官團隊也會增加或不同。
- 每個面試官獨自的面試方式或評分的重點也可能會改變。
舉例
- 應徵的職位為RD,其面試官組成與順序:HR→Team Leader→Manager。
- 應徵的職位為Manager,其面試官組成與順序:HR→Manager→VP。
- 面試過程中,面試官有權力終止面試流程,若無問題,則送應徵者往下一關卡。
原始的設計
先將會用到的類別程式碼列出:
/// <summary>
/// 應徵者介面
/// </summary>
public interface ICandidate
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets a value indicating whether this instance is lost qualification.
/// 是否失去資格,代表不用往下再面試了
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// <c>true</c> if this instance is lost qualification; otherwise, <c>false</c>.
/// </value>
bool IsLostQualification { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 人格特質評分
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The personality points.
/// </value>
int PersonalityPoints { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 技術能力評分
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The technical ability points.
/// </value>
int TechnicalAbilityPoints { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 態度評分
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The attitude points.
/// </value>
int AttitudePoints { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 潛力評分
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The potential points.
/// </value>
int PotentialPoints { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the interview result.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The interview result.
/// </value>
HireStatus InterviewResult { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets or sets the position.
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The position.
/// </value>
Position Position { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 薪資
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The payment.
/// </value>
long Payment { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 評估與結算,應徵者的面試結果、薪資狀態等等...
/// </summary>
void CalculateResult();
} public class Candidate : ICandidate
{
public bool IsLostQualification { get; set; }
public int PersonalityPoints { get; set; }
public int TechnicalAbilityPoints { get; set; }
public int AttitudePoints { get; set; }
public int PotentialPoints { get; set; }
public HireStatus InterviewResult { get; set; }
public Position Position { get; set; }
public long Payment { get; set; }
public void CalculateResult()
{
//可再透過strategy pattern來決定不同的職務該怎麼決定面試結果
switch (this.Position)
{
case Position.RD:
this.CalculateRD();
break;
case Position.Manager:
this.CalculateManager();
break;
default:
case Position.None:
break;
}
}
private void CalculateManager()
{
double points = (this.AttitudePoints + this.PersonalityPoints + this.PotentialPoints) / (double)3;
if (this.PersonalityPoints < 60 || points < 60)
{
this.InterviewResult = HireStatus.Reject;
}
else if (points >= 60 && points < 80)
{
this.InterviewResult = HireStatus.SecondRound;
}
else if (points > 90)
{
this.Payment = 100;
this.InterviewResult = HireStatus.Hire;
}
else
{
this.InterviewResult = HireStatus.WaitForOtherCandidate;
}
}
private void CalculateRD()
{
if (this.TechnicalAbilityPoints < 60)
{
this.InterviewResult = HireStatus.Reject;
}
else
{
this.InterviewResult = HireStatus.Hire;
this.Payment = 60;
}
}
} public enum HireStatus
{
/// <summary>
/// 初始值
/// </summary>
None = 0,
/// <summary>
/// 不予錄取
/// </summary>
Reject,
/// <summary>
/// 錄取
/// </summary>
Hire,
/// <summary>
/// 轉介其他部門
/// </summary>
ForwardOtherDepartment,
/// <summary>
/// 第二輪面試機會
/// </summary>
SecondRound,
/// <summary>
/// 等待其他應徵者面試完畢比較
/// </summary>
WaitForOtherCandidate
}
public enum Position
{
None = 0,
RD,
Manager
}
1.使用巢狀的if/else if來判斷應徵者的應徵職務,將每個面試官的面試方式獨立成分開的function,以便抽象的描述、設計與重用。
2.每個面試官面試完,要判斷是否要終止面試過程,還是程式碼要繼續往下執行。
缺點:
1.巢狀if/else if,可讀性差,擴充性差。
2.看不出來所謂的『面試流程』,只看的到一堆判斷。
3.未來新增應徵職位或希望改變順序,都是一件困難的事。
class OriginalCode
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ICandidate candidate = new Candidate() { Position = Position.RD };
ICandidate result = Interview(candidate);
}
/// <summary>
/// 如果是來應徵RD的,那要先經過HR, Team Leader, Manager面試。若面試過程中,出現大問題,面試官有權終止面試流程。若沒大問題,則送應徵者往下一關前進。
/// 如果是來應徵Manager的,那要經過HR, Manager, VP的面試。若面試過程中,出現大問題,面試官有權終止面試流程。若沒大問題,則送應徵者往下一關前進。
/// 每個關卡面試的邏輯都不一樣
/// 不同的職務,會有不同的面試流程
/// 未來則可能依據特殊狀況來調整面試的順序或是面試官的角色,例如RD先與Manager面試,再與Team Leader面試。或是高階RD還需要通過VP面試等等...
/// </summary>
/// <param name="candidate"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private static ICandidate Interview(ICandidate candidate)
{
var result = candidate;
if (candidate.Position == Position.RD)
{
result = InterviewByHR(result);
if (!result.IsLostQualification)
{
result = InterviewByTeamLeader(result);
if (!result.IsLostQualification)
{
result = InterviewByManager(result);
}
}
return result;
}
else if (candidate.Position == Position.Manager)
{
result = InterviewByHR(result);
if (!result.IsLostQualification)
{
result = InterviewByManager(result);
if (!result.IsLostQualification)
{
result = InterviewByVP(result);
}
}
return result;
}
return result;
}
private static ICandidate InterviewByVP(ICandidate result)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
private static ICandidate InterviewByManager(ICandidate result)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
private static ICandidate InterviewByTeamLeader(ICandidate result)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
private static ICandidate InterviewByHR(ICandidate result)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
抽象的分離職責
1.將每一個角色拆成獨立的物件,並予以相同的操作:interview。
2.每一個角色在interview後,會檢查是否將應徵者送往下一關卡,以及是否有下一關卡。
來看一下,應用責任鏈模式來設計這個case,其Class Diagram應該像這樣:
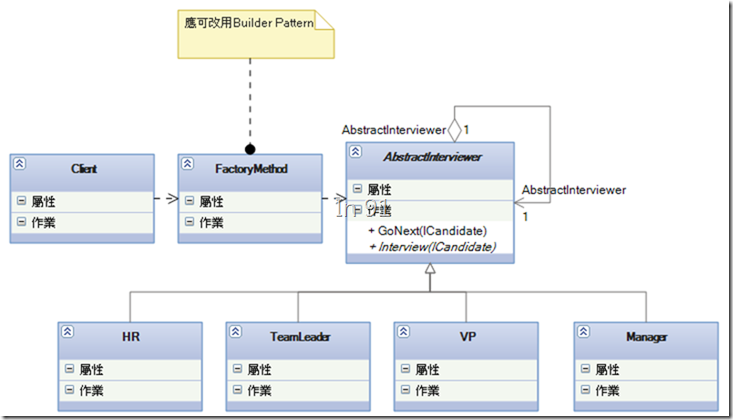
- 每一個面試官都是一種Interviewer。
- Interviewer都有一個Interview的方法,但這個interview的方法由各個子類自行決定內容,故interview()宣告成abstract。
- Interviewer將應徵者送往下一關卡的動作,宣告成GoNext()方法,且每一個面試官都應該依循同一個準則來執行。
- 在決定Interviewer的時候,應決定下一個負責的Interviewer是哪個角色。也就是圖上AbstractInterviewer自己與自己的聚合關係。
- 由一個中介的建構類來決定,面試官的組成與順序。這邊為簡單工廠模式,但其實改為使用Builder會更恰當(這就當下一篇文的伏筆吧…)
-
Client,也就是使用場景,則應只需將應徵者ICandidate丟給建構類回傳的AbstractInterviewer,呼叫interview的方法即可。
使用責任鏈模式應用來重構
1.抽象的面試官(AbstractInterviewer):將面試官的行為抽象出來
public abstract class AbstractInterviewer
{
/// <summary>
/// 定義下一個interviewer
/// </summary>
/// <value>
/// The next interviewer.
/// </value>
protected AbstractInterviewer NextInterviewer { get; set; }
public AbstractInterviewer()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="AbstractInterviewer"/> class.
/// 若傳入為null,則代表是最後一關
/// </summary>
/// <param name="nextInterviewer">The next interviewer.</param>
public AbstractInterviewer(AbstractInterviewer nextInterviewer)
{
this.NextInterviewer = nextInterviewer;
}
/// <summary>
/// 每一個子類interview的內容
/// </summary>
/// <param name="candidate">The candidate.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public abstract ICandidate InterView(ICandidate candidate);
/// <summary>
/// 往下一個interview關卡
/// </summary>
/// <param name="candidate">The candidate.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
protected ICandidate GoNext(ICandidate candidate)
{
var result = candidate;
////還有下一個interviewer且應徵人還沒失去資格時,送應徵者往下一個interview關卡
if (this.NextInterviewer != null && !result.IsLostQualification)
{
result = this.NextInterviewer.InterView(candidate);
}
result.CalculateResult();
return result;
}
}
2. Concrete面試官(包括HR, TeamLeader, Manager, VP):用來決定各個角色面試方式與評分標準
public class HR : AbstractInterviewer
{
public HR(AbstractInterviewer nextInterviewer)
{
this.NextInterviewer = nextInterviewer;
}
/// <summary>
/// HR interview的邏輯與內容
/// </summary>
/// <param name="candidate">The candidate.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public override ICandidate InterView(ICandidate candidate)
{
candidate.PersonalityPoints = 60;
Console.WriteLine("{0}面試中...人格特質:{1}", "HR", candidate.PersonalityPoints.ToString());
return this.GoNext(candidate);
}
}
public class TeamLeader : AbstractInterviewer
{
public TeamLeader(AbstractInterviewer nextInterviewer)
{
this.NextInterviewer = nextInterviewer;
}
/// <summary>
/// TeamLeader interview的邏輯與內容
/// </summary>
/// <param name="candidate">The candidate.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public override ICandidate InterView(ICandidate candidate)
{
candidate.TechnicalAbilityPoints = 70;
Console.WriteLine("{0}面試中...技術能力:{1}", "TeamLeader", candidate.TechnicalAbilityPoints.ToString());
return this.GoNext(candidate);
}
}
public class Manager : AbstractInterviewer
{
public Manager(AbstractInterviewer nextInterviewer)
{
this.NextInterviewer = nextInterviewer;
}
/// <summary>
/// Manager interview的邏輯與內容
/// </summary>
/// <param name="candidate">The candidate.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public override ICandidate InterView(ICandidate candidate)
{
candidate.PotentialPoints = 60;
Console.WriteLine("{0}面試中...潛力分數:{1}", "Manager", candidate.PotentialPoints.ToString());
return this.GoNext(candidate);
}
}
public class VP : AbstractInterviewer
{
public VP(AbstractInterviewer nextInterviewer)
{
this.NextInterviewer = nextInterviewer;
}
/// <summary>
/// VP interview的邏輯與內容
/// </summary>
/// <param name="candidate">The candidate.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public override ICandidate InterView(ICandidate candidate)
{
candidate.AttitudePoints = 80;
Console.WriteLine("{0}面試中...態度分數:{1}", "VP", candidate.AttitudePoints.ToString());
return this.GoNext(candidate);
}
}
3. 簡單工廠(FactoryMethod):依據應徵職位,決定面試官的組成與面試順序
public class FactoryMethod
{
/// <summary>
/// 依據不同職位來安排不同的面試關卡
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">The position.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static AbstractInterviewer GetInterviewers(Position position)
{
switch (position)
{
//如果應徵的職位是RD,面試關卡為:HR=>TeamLeader=>Manager
case Position.RD:
return new HR(new TeamLeader(new Manager(null)));
//如果應徵的職位是Manager
case Position.Manager:
return new HR(new Manager(new VP(null)));
default:
case Position.None:
return null;
}
}
}
4. 重構後的使用場景
class Program
{
/// <summary>
/// InterviewManager()與InterviewRD(),也可以改用strategy pattern來實作。
/// </summary>
/// <param name="args"></param>
static void Main(string[] args)
{
InterviewManager();
Console.WriteLine();
InterviewRD();
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static void InterviewRD()
{
ICandidate candidate = new Candidate { Position = Position.RD };
Interview(candidate);
}
private static void InterviewManager()
{
ICandidate candidate = new Candidate { Position = Position.Manager };
Interview(candidate);
}
private static void Interview(ICandidate candidate)
{
//簡單工廠模式可以改用builder pattern來實作更為恰當
var interviewer = FactoryMethod.GetInterviewers(candidate.Position);
interviewer.InterView(candidate);
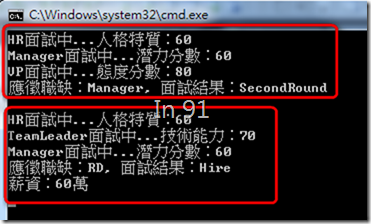
Console.WriteLine(@"應徵職缺:{0}, 面試結果:{1}", candidate.Position.ToString(), candidate.InterviewResult.ToString());
if (candidate.InterviewResult == HireStatus.Hire)
{
Console.WriteLine("薪資:{0}萬", candidate.Payment.ToString());
}
}
}
結果
結論
這一篇的應用,其實也不是所謂正規的責任鏈模式,但class diagram與pattern的設計是一致的,要解決的問題也是一致的,只是根據特有的需求來加以變化。
透過責任鏈來設計後,我們滿足了前面列的需求說明:
- 讓每個角色各司其職,不用管前後是誰,只要面試完,交給下一關卡。
- 讓使用場景不需知道面試細節,甚至不需知道面試官的組成與順序。使用場景focus的只有,把應徵者推去面試。
- 職位與面試官組成/順序的關係獨立出來,與面試細節無關,與使用場景無關。
責任鏈雖帶來以上的彈性,但也是有缺點的,責任鏈其實有點像是物件之間的方法遞迴(實際偵錯run一輪就會很有感覺了),所以責任鏈越長,可能效率會越差。
後記
寫Design Pattern文章有幾個很麻煩的地方:一個Pattern,通常是針對特定的問題/需求,累積了許多的經驗所定義出比較common的設計方式來解決,所以稱為Pattern。
如果眼前或未來沒有這樣的問題或需求,那用了只是增加複雜度,也就是所謂的over design。
而針對一個Pattern寫的文章,就得凸顯這一類的問題與需求,針對這個需求來設計sample與應用pattern後的差異。但如果一篇文章用到多個Pattern,就很容易讓讀者搞混。所以比較好懂的表達方式是,只重構該問題領域與該Pattern所屬範圍,這樣才能凸顯該Pattern的重點。
所以,很多文章,不是因為作者不懂,或是為什麼sample code有些地方明明可以設計的更漂亮,卻不用其他pattern去設計或重構。原因只是:那不是我這個Pattern要強調的重點,且我得假設眼前與未來沒有那樣的需求。
只有讀者一個一個pattern去理解,並且實際地碰到該類問題/需求,實際的去實作與設計,才能體會為什麼需要Design Pattern。所以,請饒了我吧,如果一篇文章一個應用,隨手就放了四個Pattern,那要嘛文章長到爆炸,要嘛沒人願意看完或看懂。
Sample Project:ChainOfResponsibilitySample.zip
blog 與課程更新內容,請前往新站位置:http://tdd.best/
