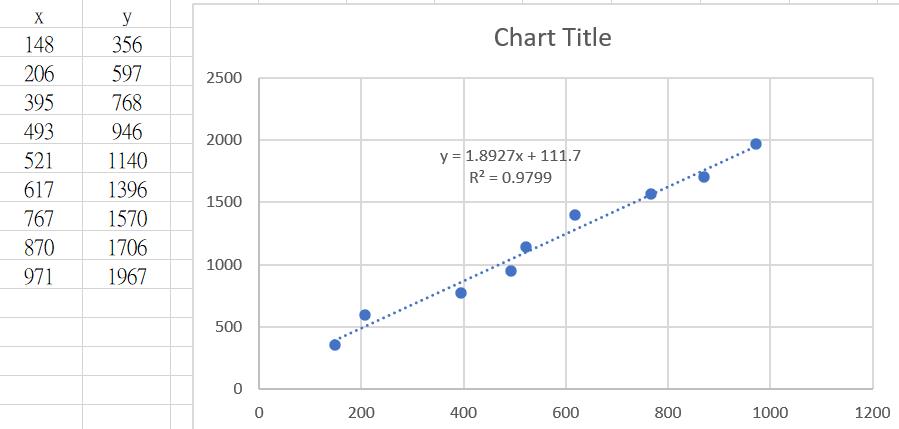
簡單的計算 Slope
先計算重心: meanX 和 meanY
Slope = (sumXY - n * meanX * meanY) / (sumX2 - n * meanX * meanX);
Shift = meanY - Slope * meanX;
#include <iostream>
void Line_Slope(double* X_tmp, double* Y_tmp , int Count_tmp, double & slope , double & shift )
{
double sum_xx = 0;
double sum_xy = 0;
double mean_x = 0;
double mean_y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Count_tmp; i++)
{
sum_xx = sum_xx + (*(X_tmp + i)) * (*(X_tmp + i));
sum_xy = sum_xy + (*(X_tmp + i)) * (*(Y_tmp + i));
mean_x = mean_x + (*(X_tmp + i)) ;
mean_y = mean_y + (*(Y_tmp + i));
}
mean_x = mean_x / (double)Count_tmp;
mean_y = mean_y / (double)Count_tmp;
slope = (sum_xy - Count_tmp * mean_x * mean_y) / (sum_xx - Count_tmp * mean_x * mean_x);
shift = mean_y - slope * mean_x;
}
int main()
{
double X_array[] = { 148,206,395,493,521,617,767,870,971 };
double Y_array[] = { 356,597,768,946,1140,1396,1570,1706,1967 };
int Count = 9;
double slope = 1;
double shift = 0;
Line_Slope(X_array, Y_array, Count, slope, shift);
std::cout << "test: " << slope << " " << shift << "\n";
std::cin.get();
}
---
使用 vector 時
void Line_Slope(const std::vector < double > &X_tmp, const std::vector < double > &Y_tmp, double& slope, double& Intercept)
{
int Count_tmp = X_tmp.size();
double sum_xx = 0;
double sum_xy = 0;
double mean_x = 0;
double mean_y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Count_tmp; i++)
{
sum_xx = sum_xx + X_tmp[i] * X_tmp[i];
sum_xy = sum_xy + X_tmp[i] * Y_tmp[i];
mean_x = mean_x + X_tmp[i];
mean_y = mean_y + Y_tmp[i];
}
mean_x = mean_x / (double)Count_tmp;
mean_y = mean_y / (double)Count_tmp;
slope = (sum_xy - Count_tmp * mean_x * mean_y) / (sum_xx - Count_tmp * mean_x * mean_x);
Intercept = mean_y - slope * mean_x;
}
int main()
{
std::vector < double > X_array = { 148,206,395,493,521,617,767,870,971 };
std::vector < double > Y_array = { 356,597,768,946,1140,1396,1570,1706,1967 };
double slope = 1;
double shift = 0;
Line_Slope(X_array, Y_array, slope, shift);
std::cout << "test: " << slope << " " << shift << "\n";
std::cin.get();
}
---
影像上用 unsigned char* 時
切記只有 0~255
#include <iostream>
void Line_Slope(unsigned char* X_tmp, unsigned char* Y_tmp , int Count_tmp, double & slope , double & shift )
{
float sum_xx = 0;
float sum_xy = 0;
float mean_x = 0;
float mean_y = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Count_tmp; i++)
{
sum_xx = sum_xx + ((float)(*(X_tmp + i)) * (float)(*(X_tmp + i)));
sum_xy = sum_xy + ((float)(*(X_tmp + i)) * (float)(*(Y_tmp + i)));
mean_x = mean_x + ((float)(*(X_tmp + i)));
mean_y = mean_y + ((float)(*(Y_tmp + i)));
}
mean_x = mean_x / (float)Count_tmp;
mean_y = mean_y / (float)Count_tmp;
slope = (sum_xy - Count_tmp * mean_x * mean_y) / (sum_xx - Count_tmp * mean_x * mean_x);
shift = mean_y - slope * mean_x;
}
int main()
{
unsigned char X_array[] = { 14,20,39,49,52,61,76,87,97 };
unsigned char Y_array[] = { 35,59,76,94,114,139,157,170,196 };
int Count = 9;
double slope = 1;
double shift = 0;
Line_Slope(X_array, Y_array, Count, slope, shift);
std::cout << "test: " << slope << " " << shift << "\n";
for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
{
std::cout << (double)(*(X_array + i)) << " " << (double)(*(Y_array + i)) << std::endl;
}
std::cin.get();
}